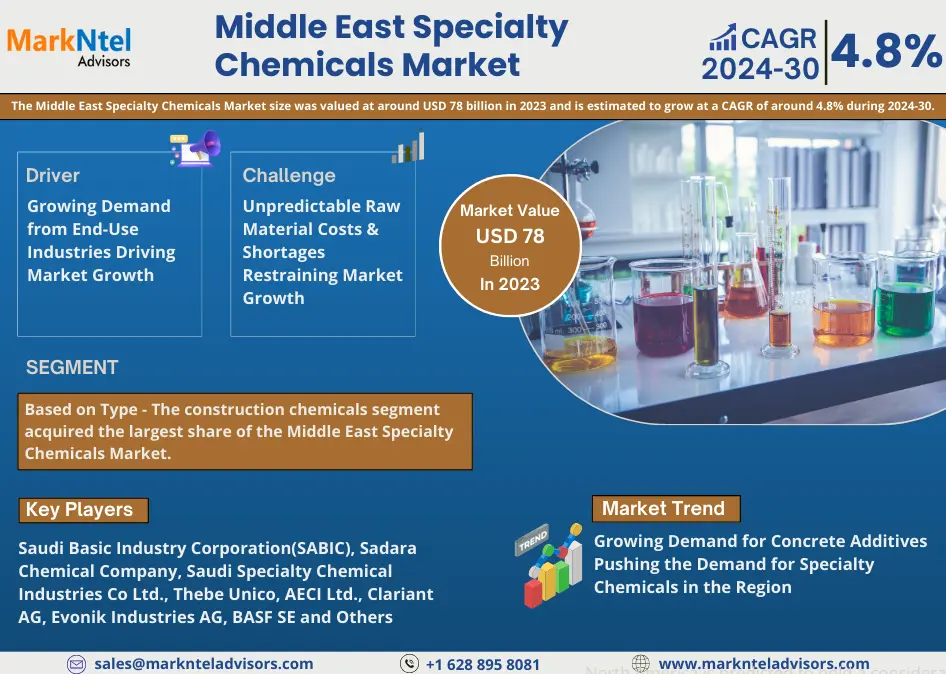
The global small satellite market size attained a value of USD 4.91 billion in 2023. The market is further expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.80% between 2024 and 2032, reaching a value of USD 18.40 billion by 2032. This significant growth is being driven by advancements in satellite technology, the increasing demand for data and connectivity, and the declining costs of satellite launches. Small satellites, including minisatellites, microsatellites, and nanosatellites, are becoming a game-changer in space exploration, Earth observation, communication, and scientific research. As industries and governments continue to invest in space technology, small satellites are poised to play an increasingly important role across a variety of sectors.
In this blog post, we will explore the key segments of the small satellite market, its major applications, regional trends, market dynamics, and the opportunities that lie ahead for this rapidly growing industry.
What Are Small Satellites?
Small satellites, often referred to as “smallsats,” are a category of spacecraft with a significantly smaller mass and size compared to traditional large satellites. They are typically defined as satellites weighing less than 500 kg, although the subcategories of smallsats include:
- Minisatellites: Satellites weighing between 100 kg and 500 kg.
- Microsatellites: Satellites weighing between 10 kg and 100 kg.
- Nanosatellites: Satellites weighing between 1 kg and 10 kg.
- Other variations: Including picosatellites (less than 1 kg) and femtosatellites (sub-100g).
The defining characteristic of small satellites is their compact size and lower cost of development and deployment, making space exploration and satellite services more accessible to a wider range of industries and nations.
Market Segmentation of Small Satellites
By Type: Minisatellites, Microsatellites, Nanosatellites, and Others
The small satellite market is primarily segmented by type, with each category serving different use cases based on size, weight, and functionality:
-
Minisatellites: With a weight range of 100-500 kg, minisatellites are often used for commercial and government applications such as communication, Earth observation, and scientific research. These satellites are large enough to carry a variety of payloads while still being more cost-effective than traditional larger satellites.
-
Microsatellites: These satellites, weighing between 10 kg and 100 kg, are increasingly popular for commercial applications, including satellite communications, Earth monitoring, and remote sensing. Their smaller size allows for quicker development and launches at a fraction of the cost of traditional satellites.
-
Nanosatellites: Weighing 1 kg to 10 kg, nanosatellites are the most cost-effective and agile form of small satellite, often deployed in constellations for services like global internet coverage, weather forecasting, and GPS navigation. Their small size makes them ideal for academic, research, and start-up ventures aiming to capitalize on space technology.
-
Others: Emerging small satellite types such as picosatellites (under 1 kg) are used in highly specialized applications like advanced scientific experiments, space weather monitoring, and technology testing.
By Application: Earth Observation, Satellite Communication, Science and Exploration, Mapping and Navigation, and Others
The small satellite market is also segmented by application, with a wide range of industries relying on small satellite technology for various purposes:
-
Earth Observation and Remote Sensing: Small satellites play a crucial role in environmental monitoring, disaster management, agriculture, and climate change research. Their ability to provide real-time imagery and data from space enables governments and organizations to track changes in the Earth’s surface, oceans, and atmosphere.
-
Satellite Communication: Small satellites are increasingly used in global broadband, telecommunications, and data transmission. Notable projects like SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb are deploying constellations of small satellites to provide internet access to underserved areas and improve global connectivity.
-
Science and Exploration: Small satellites are becoming vital tools for space research, exploration, and experimentation. These satellites help gather data on cosmic phenomena, space weather, and planetary exploration while also reducing the cost of scientific missions.
-
Mapping and Navigation: With the growing demand for GPS systems and geospatial data, small satellites are increasingly used to enhance global positioning systems (GPS) and provide high-accuracy mapping and navigation solutions, benefiting industries like logistics, transportation, and agriculture.
-
Others: Other applications of small satellites include defense and military purposes, disaster response, and infrastructure monitoring. Small satellites are used to track and monitor potential threats, assist in emergency communication, and evaluate the health of infrastructure such as pipelines, bridges, and dams.
By End Use: Government, Commercial, and Others
The small satellite market also sees segmentation based on end-use:
-
Government: Government agencies, such as NASA, ESA, and ISRO, continue to be major users of small satellites for national security, Earth observation, and space exploration. Many countries are investing in small satellite constellations to enhance their ability to monitor global events, improve communication, and gather scientific data.
-
Commercial: The commercial sector is a growing driver of the small satellite market, with companies focusing on telecommunications, data collection, and satellite-as-a-service. These businesses are increasingly interested in deploying smallsats to offer new, low-cost services, such as global internet or real-time Earth monitoring.
-
Others: Educational institutions and non-profit organizations also use small satellites for research, technology development, and humanitarian projects, often in collaboration with government or commercial entities.
Regional Analysis of the Small Satellite Market
North America
North America, particularly the United States, is the largest market for small satellites, driven by a well-established space industry, major private players like SpaceX and Rocket Lab, and strong government-backed initiatives. The demand for satellite communication, remote sensing, and Earth observation services is fueling growth in this region.
Europe
Europe is home to several prominent satellite manufacturing companies, including Airbus Defence and Space and Thales Alenia Space. The European Space Agency (ESA) also plays a significant role in supporting small satellite missions. There is an increasing focus on environmental monitoring, science, and exploration in the region.
Asia-Pacific
Countries like India, China, and Japan are rapidly expanding their space programs and investing heavily in small satellite technology. ISRO‘s Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) and China’s ambitious space programs are driving demand for small satellite technology across the region.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa, along with Latin America, are emerging as significant markets, particularly for remote sensing and telecommunications. Many countries in these regions are looking to small satellites to enhance their capabilities in agriculture, climate monitoring, and communications.
Market Dynamics: Drivers, Challenges, and Opportunities
Key Drivers of Market Growth
- Declining Launch Costs: The decreasing cost of launching small satellites due to advances in reusable rocket technology and more affordable access to space is driving growth.
- Increasing Demand for Connectivity: The need for global internet coverage and data transmission, particularly in underserved regions, is fueling the demand for small satellite constellations.
- Advancements in Miniaturization: Technological advancements in satellite design, payload miniaturization, and propulsion systems are making small satellites more capable and versatile.
Challenges
- Space Debris: The proliferation of small satellites poses concerns about space debris and the potential for collisions in crowded orbits.
- Regulatory Challenges: As more countries and companies launch small satellites, regulatory frameworks around frequency allocation, orbital management, and satellite tracking will become increasingly important.
Opportunities
- New Market Applications: Emerging industries such as Internet of Things (IoT), global broadband, and precision agriculture are creating new opportunities for small satellites.
- Private Sector Investment: Increased private sector investment in space exploration and satellite deployment opens new avenues for innovation and market expansion.
Competitive Landscape
Key players in the small satellite market include companies like SpaceX, OneWeb, Planet Labs, Astra, and Rocket Lab, as well as traditional aerospace companies like Airbus and Lockheed Martin. These companies are focused on driving technological innovation, reducing launch costs, and expanding satellite constellations to offer global services in communication, Earth observation, and beyond.